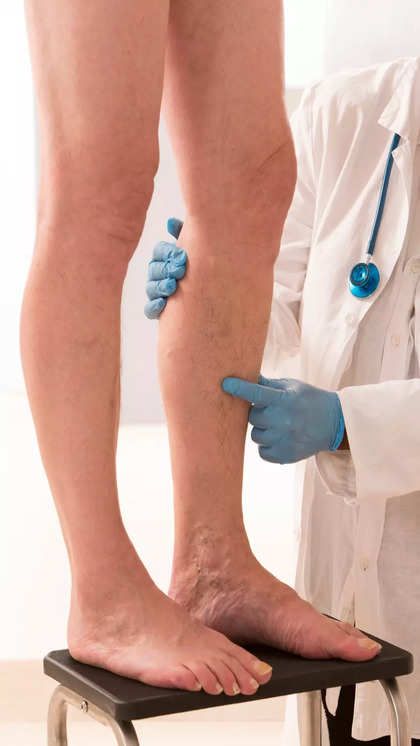
Thrombosis, also known as a blood clot, is a dangerous condition that can have serious health consequences. This condition results in the formation of a blood clot in a blood vessel, leading to death and is the third leading cause of death in industrialized countries.
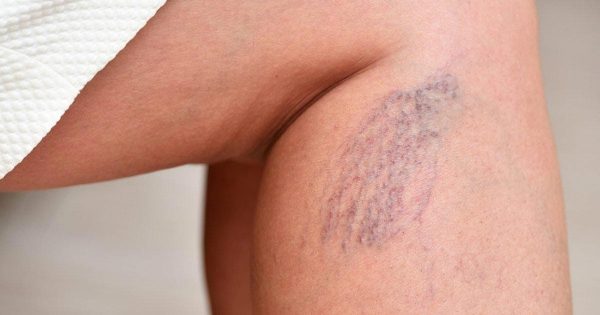
Recognizing the symptoms of various conditions, including thrombosis, is crucial for our health. This condition can lead to the formation of blood clots in veins and arteries and can be fatal. Therefore, it’s important to know the associated signs for timely detection. By being informed, we can take steps to protect our health and minimize the risk of serious complications.
What is thrombosis?
Thrombosis is a serious condition characterized by the formation of a clot in a blood vessel (vein or artery). If the vein is affected, it is called venous thrombosis or phlebitis. If the artery is affected, it is called arterial thrombosis.
Thrombosis can lead to fatal complications, such as pulmonary embolism, in which the clot breaks away and travels into the pulmonary artery. It can also cause heart attacks, strokes, and other vascular accidents in the lower extremities or intestines. Therefore, it’s important to take thrombosis seriously and know the symptoms to protect your health.
How are the different types of thrombosis characterized?
Two types of thrombosis that can also cause existing complications. Venous thrombosis, or phlebitis, is a disease of a superficial or deep vein, while arterial thrombosis can block an artery and become dangerous if it no longer supplies fluid to an area of the body.
What are the causes of thrombosis?
The causes of thrombosis can vary depending on whether an artery or a vein is affected. Arterial thrombosis can be caused by damage to the artery wall, such as atherosclerosis, or by risk factors such as cigarette smoking or hormonal contraceptives. Causes of venous thrombosis can include cancer, infections, inflammation, varicose veins, prolonged sitting, injuries, surgery, or prolonged immobilization.
What are the symptoms of a vein or artery blockage?
The symptoms of venous thrombosis depend on the location of the thrombosis. If a thrombosis occurs in a lower extremity, symptoms may include pain, hardening, redness, and warmth in the affected area, a bluish or whitish discoloration, and edema. However, in 50% of cases, deep vein thrombosis may be asymptomatic. If it is an arterial thrombosis, symptoms may occur depending on the area affected. For example, if the thrombosis affects a cerebral artery, the symptoms may be similar to those of a stroke. If the thrombosis affects a coronary artery, the symptoms may be similar to those of a heart attack. Arterial thrombosis of the lower extremities can cause severe pain, pallor, coldness, and pulselessness in the affected area. If a thrombosis forms in the arteries supplying the digestive tract, it can cause persistent abdominal pain.
Who is most affected by this disease?
According to Dr. Catherine Solano, one in a thousand people can be affected by venous or arterial thrombosis, and among these people, 3 in 1,000 are over 80 years old. A genetic predisposition can increase the risk of developing thrombosis. People with blood clotting disorders are also at higher risk of developing thrombosis. Smoking and an excessively sedentary lifestyle can also increase the risk. Certain conditions such as diabetes, heart failure, pancreatic cancer, breast cancer, or venous congestion can also increase the risk of thrombosis. Women taking hormonal contraceptives and people taking corticosteroids may also be at risk. Events such as prolonged immobilization or long journeys can also cause thrombosis.
How is thrombosis diagnosed?
If you experience symptoms of thrombosis, it is essential to see a doctor. They will perform various imaging tests, such as arteriography or phlebography, to diagnose the pathology. Blood tests can also reveal D-dimer levels, an indicator of blood clot formation.
How is venous thrombosis treated?
Treatment varies depending on the type of thrombosis. If the thrombosis occurs in the lower extremities, treatment consists of injections of anticoagulants and pain-relieving medications. For deep injuries, doctors administer daily blood thinners to prevent the clot from spreading. In severe cases of obstruction, fibrinolytics may be administered to dissolve the clot. To prevent complications, wearing compression stockings for two years is recommended. If the clot becomes lodged in the deep veins and there is a risk of pulmonary embolism, placement of a vena cava filter may be necessary.
How is arterial thrombosis treated?
The treatment of arterial thrombosis depends on its location. In the case of a blocked artery, rapid intervention is required to clear the artery and maintain the function of vital organs. If the thrombosis leads to a heart attack, a fibrinolytic serum is administered to relieve the obstruction. Similar treatment measures are also initiated in the case of a stroke.
How can you prevent venous thrombosis?